
Try to memorize this chart so that you don’t struggle to categorize your sub-accounts properly. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. A personal account is created and used for the personal needs of a single person, and an impersonal account can be shared with other people. A special board committee found “no evidence of fraud or misconduct on the part of management or the board of directors,” the company said Nov. 5.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Since this account does not represent any tangible asset, it is called nominal or fictitious account. All kinds of expense account, loss account, gain account or income accounts come under the category of nominal account. For example, rent account, salary account, electricity expenses account, interest income account, etc.
II. Impersonal Accounts
So let’s explore the different types of accounts in accounting. And in doing so, you will know which ones to use in your business for effective bookkeeping. Valuation account (also known as contra cost reconciliation in construction projects account) is an account which is used to report the carrying value of an asset or liability in the balance sheet. A popular example of valuation account is the accumulated depreciation account.
Solved Example on Types of Accounts
- Current liabilities include accounts payable (amounts owed to vendors that have granted credit terms) and other payables like income tax, payroll taxes, and sales tax, as well as accruals such as wages payable.
- Hence maintaining accounts definitely helps to make quick decisions in business.
- These classifications help students to cover the area adequately and learn the concepts clearly.
- There are mainly three subfields of accounting, such as Cost Accounting, Management Accounting, and Financial Accounting.
- Examples of nominal accounts include sales, purchases, gains on asset sales, wages paid, and rent paid.
This is because ‘debtors’ belong to individuals or entities and personal accounts specifically serve the purpose of calculating balances due to or due from such 3rd parties. We gather and convert all the daily transactions into financial statements, balance sheet, income statements, and cash flow statements. Certain companies might keep several different ledgers, such as those for different types of balance sheets and statement accounts, such as Sales accounts, Payroll accounts, and more.
A company, therefore, has to select the accounts and account groupings which can summarize the volumes of its accounting data. Such data is critical in the preparation of a company’s financial statements. In addition, the decisions a company makes are premised upon the data. The chart of accounts is a structured list of all accounts used by a company to record its financial transactions. It is essential for organizing financial information, facilitating financial reporting, and enabling comparisons between businesses. The chart of accounts can be customized to suit the specific needs of different industries and organizations.
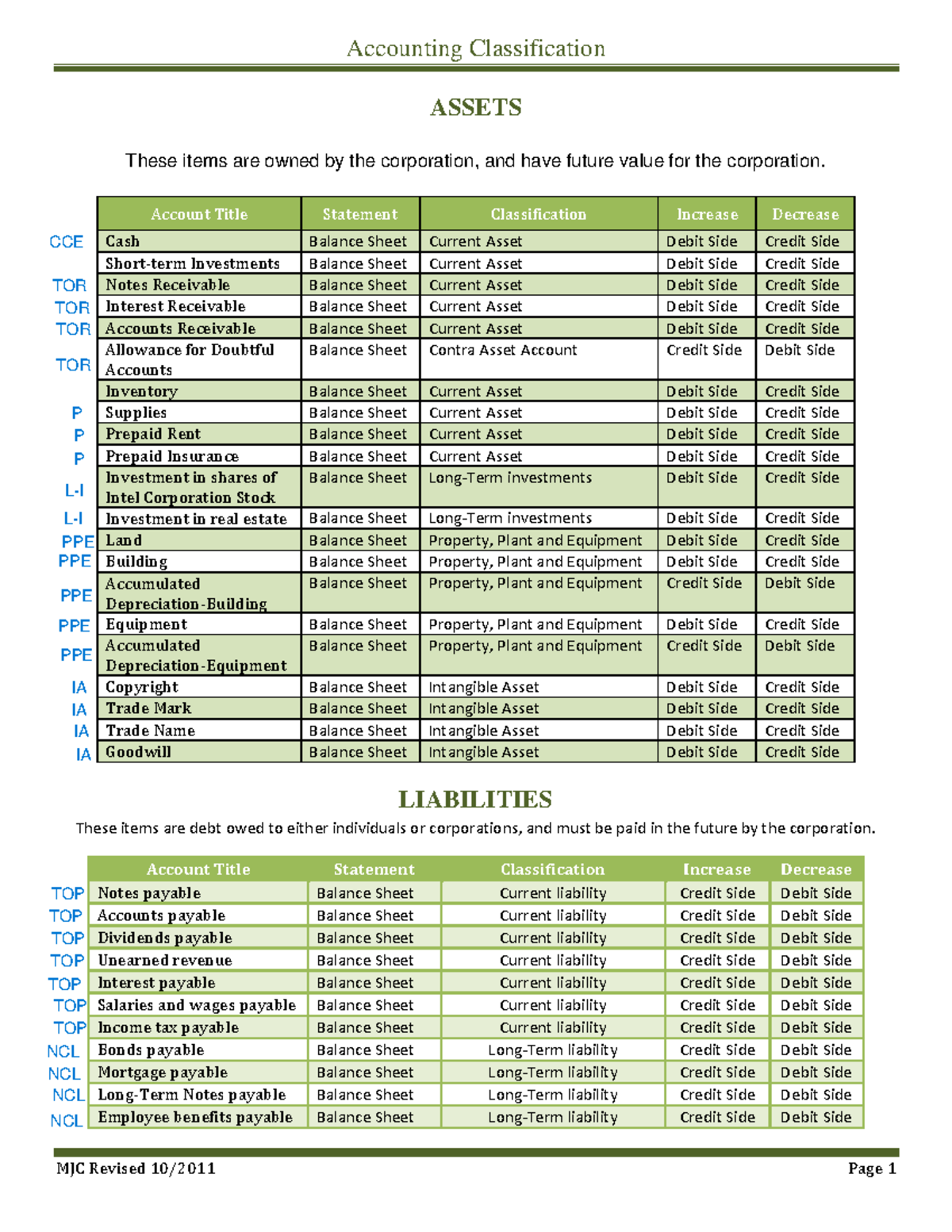
Due to its more holistic approach, the modern classification of accounts (assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses & capital) has gained more followers than the traditional classification (real, personal & nominal). Understanding the types of accounts in accounting (along with the so-called golden rule of accounting of how debits and credits work) is an essential step to confidently taking charge of your small business’ finances. So join us as we share the five different types of accounts that you need to know about as a small business owner. Real accounts are accounts related to assets or properties (both tangible and intangible) owned by a business enterprise. A separate account for each asset is maintained to account for increases and decreases in that asset. Examples of real accounts include cash account, inventory account, investment account, plant account, building account, goodwill account, patent account, copyright account etc.
Businesses using accrual-based accounting need one since the income statement records sales and purchases, not cash payments. Tracking how much cash moves in and out of the company shows whether the company has enough money on hand to make loan payments or cover payroll. If the cash flowing in is significantly less than the income, it’s possible the company’s not doing a good job collecting on accounts receivable. The cash-flow classifications include cash from investments, cash from operations and cash from financing. When you buy or sell goods and services, you must update your business accounting books by recording the transaction in the proper account. This shows you all the money coming into and going out of your business.
When you claim depreciation on the software’s loss of value due to age, all the software should depreciate at roughly the same rate. Recording all the programs in one asset classification makes it simple to apply depreciation to the whole class. In the preparation of the above, financial accounting uses a bunch of accounting principles.