Dividends, whether in cash or in stock, are the shareholders’ cut of the company’s profit. They also are a reward for holding the stock rather than selling it. A company may issue a stock dividend rather than cash if it doesn’t want to deplete its cash reserves. When the small stock dividend is declared, the market price of $5 per share is used to assign the value to the dividend as $250,000 — calculated by multiplying 500,000 x 10% x $5.

Understanding Dividends: Price Implications
Owners of both common and preferred shares may receive a dividend, but the dividend for preferred shares of a stock are usually higher, often significantly so. Companies that pay unusually high dividends may not be able to sustain them, and if dividends are cut, it might send the stock price tumbling. Dividend yield essentially tells you how much return you’re getting for the price of the stock. It also allows you to compare the dividends of stocks with different prices, as well as other interest-bearing securities, like bonds or CDs. As the business does not have to pay a dividend, there is no liability until there is a dividend declared. As soon as the dividend has been declared, the liability needs to be recorded in the books of account as a dividend payable.
How Dividend is Recorded and Presented in the Financial Statements
On average, dividend-paying stocks return 1.91% of the amount you invest in the form of dividends, which can provide a higher return than some high-yield savings accounts. Dividend stocks do not offer the same security of principal as savings accounts, though. A stock dividend is a dividend paid as shares of stock instead of cash. You can sell these dividend shares for an immediate payoff, or you can hold them. A stock dividend functions essentially like an automatic dividend reinvestment program (more on that below). For example, assume a company has $1 million in retained earnings and issues a 50-cent dividend on all 500,000 outstanding shares.
- Similarly, when interest rates are low, investors may re-allocate their funds from interest-bearing assets into more productive dividend-paying stocks.
- This simple set-it-and-forget-it tool is one of the easiest ways to put the power of time and compounding value to work in your favor.
- These techniques rely on anticipated future dividend streams to value shares.
- Dividends are commonly distributed to shareholders quarterly, though some companies may pay dividends semi-annually.
- On the payment date, the company deposits the funds for disbursement to shareholders with the Depository Trust Company (DTC).
- If you own one share of stock that’s valued at $100, a 5% annual dividend yield means the company will pay you $5 each year in dividend income.
How to Buy Dividend-Paying Investments
Similarly, when interest rates are low, investors may re-allocate their funds from interest-bearing assets into more productive dividend-paying stocks. If you buy and sell stock through a broker, dividend payments are almost always deposited directly into your brokerage account. Otherwise, a check in the amount of the dividend payment is mailed to you on the payment date. 1The S&P 500® Total Return Index assumes reinvestment of dividends, includes capital gains and does not reflect the effect of taxes and fees. Indexes are unmanaged, do not incur fees or expenses, and cannot be invested in directly. Despite these risks, dividend-paying stocks tend to provide income while still allowing for the potential of stock price appreciation.

Early, an UTMA/UGMA investment account managed by an adult custodian until the minor beneficiary comes of age, at which point they assume control of the account. Early Payday depends on the timing of the submission of the payment file from the payer and fraud prevention restrictions. Funds are generally available on the day the payment file is received, up to 2 days earlier than the scheduled payment date. Funding for education can come from any combination of options and a J.P. Morgan Advisor can help you understand the benefits and disadvantages of each one. Compare between 529 Plans, custodial accounts, financial aid and other education options to help meet your goals.
How are dividends paid out?
Retained earnings are the amount of money a company has left over after all of its obligations have been paid. Retained earnings are typically used for reinvesting in the company, paying dividends, or paying down debt. Exxon’s growing earnings and cash flow enable it to return dividends account more money to shareholders in dividends and buybacks. It returned a peer-leading $32.4 billion last year, including $14.9 billion in dividends and $17.4 billion in share repurchases. The company has consistently increased its dividend for a peer-leading 41 straight years.
- Moreover, focusing on dividend growth — a company’s history and ability to raise its stock dividend — often proves more profitable.
- Lack of diversification always exposes investors to increased volatility.
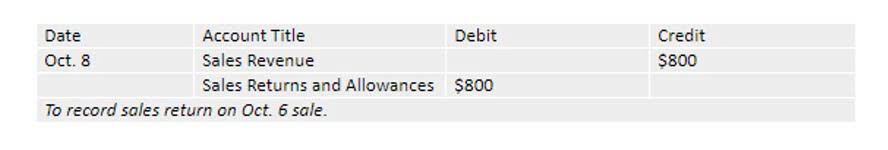
- The dividends that a company pays out are recorded and presented in its financial statements in two different steps.
- Once an investor reaches age 59½ and has held the account for at least five years, they can withdraw their earnings tax-free, providing a significant tax advantage in retirement.
- Dividend income is a bit like earning interest from a bank in exchange for holding your money in a savings account.
Morgan Private Client Advisor who will help develop a personalized investment strategy to meet your evolving needs. Easily research, trade and manage your investments online all conveniently on Chase.com and on the Chase Mobile app®. Morgan online investing is the easy, smart and low-cost way to invest online. Whether you choose to work with an advisor and develop a financial strategy or invest online, J.P. Morgan offers insights, expertise and tools to help you reach your goals.
Dividends in Accounting
- But the company’s business came under pressure, and its shares fell to $50—although it’s still paying $5 in annual dividends.
- We have been adding small tranches of Air Products and Chemicals (APD) over the last few months but are looking to trim back the high-cost shares as the stock price moves higher.
- There are ways to avoid paying taxes on dividends right away or avoid paying them at all.
- We made a handful of trades in March, with a total of three sells and three buys that included five companies and one Certificate of Deposit.
- While the yields can be attractive, the highest-paying dividend stocks sometimes overcompensate for risk.
Are Brokerage Accounts Taxed? Investing U.S. News – U.S News & World Report Money
Are Brokerage Accounts Taxed? Investing U.S. News.
Posted: Mon, 20 Nov 2023 20:15:04 GMT [source]